How Does Automated Temperature Monitoring Support HACCP Compliance?
Automated temperature monitoring directly addresses one of HACCP’s most critical control points by providing continuous, verifiable temperature tracking across food operations. HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic preventive approach to food safety that identifies and controls biological, chemical, and physical hazards at specific stages of production, storage, and distribution. Temperature control stands as a fundamental critical control point because improper temperatures create ideal conditions for bacterial growth and contamination.
The Limitations of Manual Temperature Checks
Traditional manual temperature checks leave gaps in monitoring coverage and introduce human error into HACCP compliance records. These limitations can compromise the effectiveness of the HACCP system and increase the risk of food safety violations.
The Benefits of Automated Temperature Monitoring
Automated temperature monitoring systems eliminate these vulnerabilities by using wireless sensors and data loggers to track temperatures 24/7 in refrigerators, freezers, production areas, and transport vehicles. These systems offer several advantages over manual checks:
- Continuous monitoring: Temperatures are constantly monitored without any gaps or interruptions.
- Real-time alerts: Immediate notifications are sent when temperatures go outside safe ranges.
- Accurate records: Automated documentation eliminates the possibility of human error in compliance records.
- Audit-ready reports: Reports are generated automatically in a format required by regulatory authorities.
The technology transforms food safety from a reactive checklist into a proactive, data-driven process that protects consumers and businesses simultaneously.

What Is Automated Temperature Monitoring and How Does It Work?
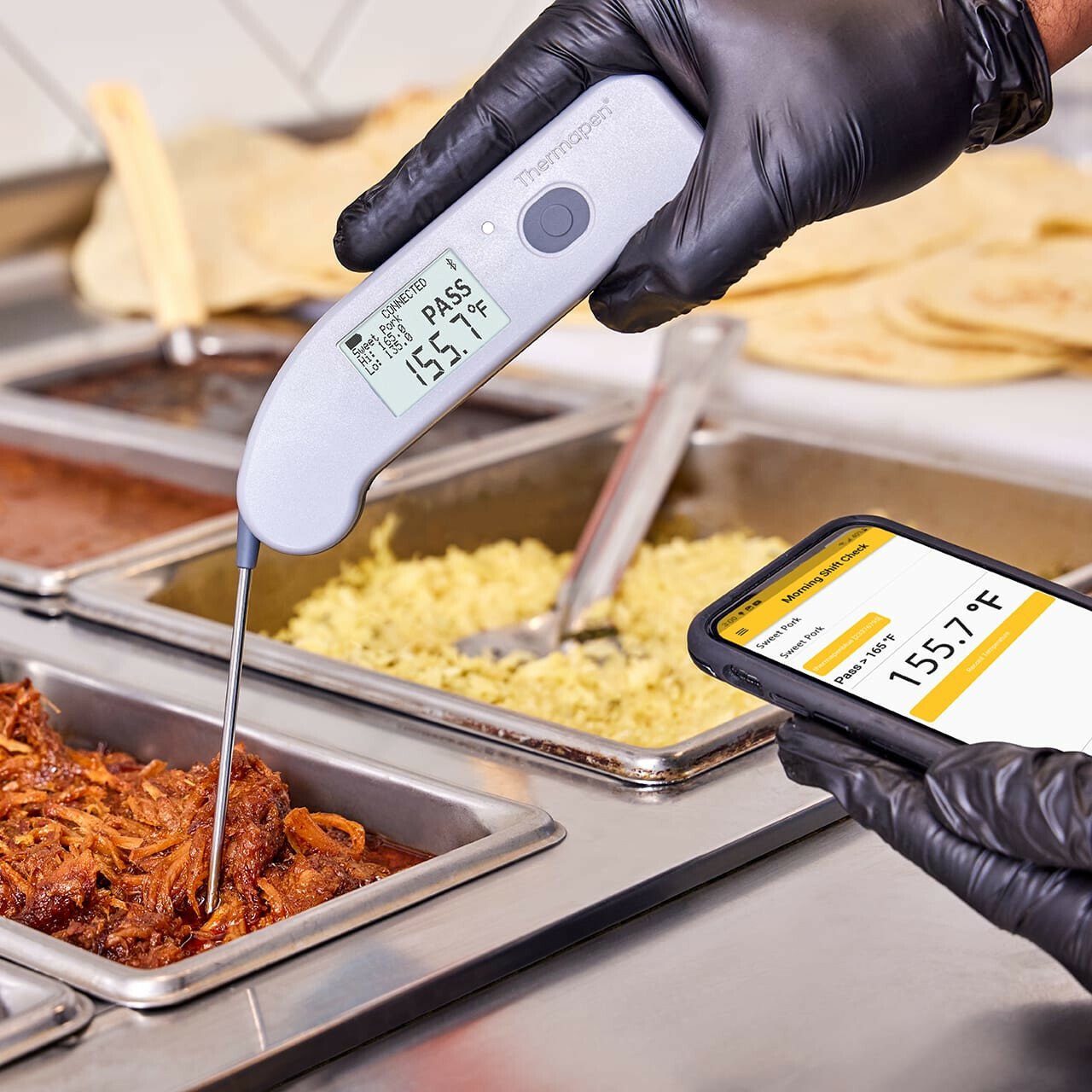
Automated temperature monitoring uses automated temperature sensors and digital technology to track temperature conditions continuously without manual intervention. These systems deploy strategically placed sensors throughout food facilities—from cold storage rooms to production lines—that measure ambient and product temperatures at regular intervals, typically every few minutes.
How Automated Temperature Monitoring Works
The technology relies on wireless transmitters that send temperature readings from sensors to a central monitoring platform or cloud-based system. This creates a network of connected devices that capture real-time data across multiple zones simultaneously. When temperatures shift outside preset critical limits, the system immediately triggers alerts via SMS, email, or mobile app notifications.
Key Components of Automated Temperature Monitoring
- Data loggers: These form another essential component, storing temperature records automatically for compliance documentation. Many systems offer built-in memory that preserves data even during power outages. An example of such a device is the MX1101 data logger from Onset, which is designed for precise temperature tracking.
- Sensors: The sensors themselves vary based on application needs:
- Probe sensors for measuring internal food temperatures
- Ambient sensors for monitoring air temperature in storage areas
- Surface sensors for refrigeration units and equipment
- Immersion sensors for liquid products and tanks
Each sensor type connects to the monitoring network through wired or wireless protocols, with wireless options providing greater flexibility for retrofitting existing facilities without extensive infrastructure changes.
Why Is Temperature Control Crucial for HACCP Compliance?
Temperature control is one of the most important critical control points in HACCP systems because it directly affects whether harmful pathogens can grow to dangerous levels. When food products stay within the “danger zone” of 5°C to 60°C for too long, bacteria like Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli can double in number every 20 minutes, turning safe products into carriers of foodborne illnesses.
HACCP protocols set specific temperature limits for each stage of handling food—from receiving raw materials to processing, storing, and distributing. These limits aren’t random; they’re scientifically determined boundaries that stop bacterial growth and keep the product intact. A refrigerated storage unit running at 6°C instead of the required 4°C may seem like a small issue, but this 2-degree difference can significantly speed up spoilage and pathogen growth.
The effects of temperature failures go beyond immediate health dangers. One single temperature mistake during transport can ruin entire batches of products, resulting in expensive recalls, regulatory fines, and loss of consumer trust. HACCP compliance requires concrete evidence that temperature controls stayed effective throughout the entire supply chain—a demand that manual monitoring often fails to meet consistently.
Key temperature-related risks include:
- Rapid multiplication of pathogenic bacteria in the danger zone
- Loss of product quality and nutritional value
- Increased likelihood of regulatory non-compliance
- Potential for widespread contamination across multiple batches
How Does Automated Temperature Monitoring Enhance Accuracy Compared to Manual Checks?
Automated temperature monitoring eliminates the inconsistencies inherent in manual temperature logging, where readings depend on individual diligence and timing. Manual checks create gaps in surveillance—temperatures fluctuate between scheduled inspections, leaving critical periods unmonitored when hazardous conditions may develop undetected.
1. Reducing Human Error
Human error reduction stands as the primary advantage of automation. Staff members may forget readings, record incorrect values, or face distractions during busy service periods. Handwritten logs suffer from illegible entries, transposed numbers, and retrospective “pencil whipping” where employees fill in missing data from memory. These practices compromise data integrity and expose businesses to compliance failures during audits.
2. Continuous Monitoring for Comprehensive Data
Continuous monitoring through automated systems captures temperature data every few minutes around the clock. Sensors transmit readings directly to digital platforms, creating tamper-proof records that satisfy regulatory requirements for How Automated Temperature Monitoring Improves HACCP Compliance. The technology delivers precision typically within ±0.1°C, far exceeding the accuracy of handheld thermometers subject to calibration drift and user technique variations.
3. Uncovering Insights Through Data Analysis
Data accuracy improves dramatically when systems log thousands of data points daily versus the handful captured through manual spot checks. This comprehensive surveillance reveals temperature trends, identifies equipment malfunctions before they cause product loss, and provides verifiable evidence that critical limits remained within safe parameters throughout storage and production cycles.
How Automated Monitoring Supports Regulatory Documentation and Reporting
Automated temperature monitoring systems generate HACCP-compliant reports instantly, eliminating the need for manual data compilation and reducing documentation errors. These systems capture every temperature reading with timestamps, creating comprehensive audit trails that demonstrate continuous compliance with food safety regulations.
The technology produces verifiable documentation that meets regulatory requirements without additional staff effort. When inspectors arrive, businesses can immediately access detailed temperature logs spanning weeks, months, or years. This instant retrieval capability proves invaluable during audits, as it demonstrates proactive safety measures rather than reactive responses to violations.
Advantages of Digital Records for Regulatory Compliance
Digital records provide several advantages for regulatory compliance:
- Tamper-proof data storage that prevents unauthorized alterations to temperature records
- Automated timestamping that creates chronological evidence of temperature control measures, a process akin to secure file timestamping
- Customizable reporting formats that align with specific regulatory body requirements
- Searchable databases that allow quick identification of specific dates, times, or temperature events
The Strategic Advantage of Historical Data Accessibility
Historical data accessibility transforms compliance from a burden into a strategic advantage. Businesses can analyse long-term temperature trends to identify equipment issues before they cause safety violations. The systems maintain complete records without physical storage requirements, making it simple to demonstrate compliance patterns over extended periods. Regulatory bodies increasingly expect digital documentation standards, and automated monitoring systems meet these evolving expectations while reducing administrative workload.
Moreover, the capability of these systems to generate comprehensive audit logs is not just limited to food safety regulations. Similar principles apply in other sectors as well, such as healthcare where HIPAA audit logs are essential for ensuring compliance during PHI transfers.
How Does Automation Improve Operational Efficiency and Employee Accountability?
1. Significant Labour Cost Reduction
Automated temperature monitoring delivers significant labour cost reduction by eliminating the need for staff to manually check and record temperatures multiple times per shift. Food businesses typically save 2-4 hours of labour daily per facility, allowing employees to focus on value-added tasks like food preparation, customer service, and quality control activities that directly impact business outcomes.
2. Transforming Safety Culture
The technology transforms safety culture by making temperature compliance visible and measurable across all shifts. Real-time alerts notify designated staff immediately when temperatures drift outside safe ranges, creating clear ownership and response protocols. This instant notification system removes ambiguity about who is responsible for corrective actions and when interventions are needed.
3. More Effective Employee Training
Employee training becomes more effective when automated systems provide concrete data showing the consequences of delayed responses or improper storage practices. New staff members can review historical temperature trends to understand seasonal patterns, equipment performance, and critical periods requiring extra vigilance. The systems create an objective record of compliance that supports performance reviews and identifies areas where additional training may be beneficial.
4. Establishing Accountability Without Punishment
Automated monitoring establishes accountability without creating a punitive environment. Staff receive immediate feedback through alerts rather than discovering problems during end-of-shift checks, enabling proactive corrections before products are compromised. This approach builds confidence and competence simultaneously, as employees learn to trust the technology whilst developing stronger food safety instincts.
What Are the Broader Benefits for Food Quality and Brand Reputation?
Automated temperature monitoring directly impacts product consistency by maintaining precise thermal conditions throughout processing and storage. When temperatures remain stable within critical limits, food products retain their intended flavour profiles, textures, and visual appeal batch after batch. A bakery using automated systems ensures pastries achieve the same golden crust every time, whilst a dairy processor maintains the exact firmness and taste consumers expect from their yoghurt products.
Nutritional value preservation depends heavily on controlled temperature environments. Heat-sensitive vitamins like B and C degrade rapidly when products experience thermal fluctuations, yet automated monitoring prevents these losses by catching deviations within seconds. Fresh produce maintains higher vitamin content, frozen meals preserve their fortified nutrients, and chilled proteins retain their amino acid profiles when systems actively guard against temperature abuse.
The connection between reliable temperature control and brand trust becomes evident during crisis prevention. Automated systems that flag potential hazards before products reach consumers prevent costly recalls that damage reputation irreparably. A single recall can cost businesses millions in direct expenses whilst eroding customer confidence for years. Real-time monitoring creates a protective barrier against spoilage and contamination risks, demonstrating to consumers and regulators alike that food safety remains the priority. This commitment to quality through technology strengthens market position and customer loyalty.
Where Are Automated Temperature Monitoring Systems Commonly Used Across the Food Supply Chain?
Automated temperature monitoring systems serve critical functions throughout every stage of the food supply chain.
1. Food Manufacturing
Food manufacturing facilities deploy these systems in production lines, processing areas, and blast chillers where precise temperature control prevents bacterial growth during cooking, cooling, and packaging operations. Sensors track thermal conditions in mixing tanks, pasteurisation equipment, and fermentation chambers to maintain product consistency and safety.
2. Cold Storage
Cold storage environments represent another primary application area. Distribution centres, walk-in freezers, and refrigerated warehouses rely on wireless sensors to monitor multiple zones simultaneously. These systems detect temperature fluctuations in real-time, protecting inventory worth thousands of pounds from spoilage caused by equipment malfunctions or door breaches.
3. Transportation Monitoring
Transportation monitoring extends HACCP compliance beyond static facilities. Refrigerated lorries, shipping containers, and delivery vans use portable data loggers and GPS-enabled sensors to document temperature conditions during transit. This capability proves essential for maintaining the cold chain from supplier to retailer, particularly for highly perishable items like seafood, dairy products, and vaccines.
4. Restaurants and Commercial Kitchens
Restaurants and commercial kitchens install monitoring devices in prep areas, display cases, and storage units to satisfy health department requirements.
5. Healthcare Facilities
Healthcare facilities similarly employ these systems in patient food services, pharmacies storing temperature-sensitive medications, and blood banks. Each application area benefits from continuous surveillance that manual checks cannot provide.
In particular, the handling of temperature-sensitive medications in pharmacies requires strict adherence to temperature control guidelines. Furthermore, transportation of such items must also follow stringent protocols to ensure their efficacy upon arrival. This is particularly crucial when dealing with vaccines which require specific storage temperatures to maintain their effectiveness.
What Features Make Automated Temperature Monitoring Solutions Effective for HACCP Compliance?
1. High accuracy sensors (±0.1°C)
High accuracy sensors (±0.1°C) form the foundation of effective automated monitoring systems. In critical zones like vaccine storage units, blast chillers, and ready-to-eat food preparation areas, temperature variations of even 0.5°C can accelerate bacterial growth or compromise product integrity. Precision sensors detect these minute fluctuations before they escalate into HACCP violations, providing food safety managers with the exact measurements needed to demonstrate control over critical control points during regulatory audits.
2. Data logging capabilities
Data logging capabilities transform raw temperature readings into actionable intelligence for HACCP compliance. These systems automatically record measurements at predetermined intervals—typically every 1-15 minutes—creating an unbroken chain of custody for temperature data. The logged information enables food safety teams to:
- Identify recurring temperature spikes during specific production shifts
- Analyse cooling curves to verify equipment performance meets HACCP parameters
- Generate trend reports that predict equipment failures before they occur
- Provide auditors with timestamped evidence of continuous monitoring
Comprehensive logging eliminates the gaps inherent in manual record-keeping, where staff might record temperatures only 2-3 times per shift. This continuous documentation proves particularly valuable when investigating customer complaints or responding to regulatory inquiries, as historical data reveals exactly when and where temperature deviations occurred throughout the cold chain.

Conclusion
How does automated temperature monitoring transform food safety beyond compliance requirements? The technology fundamentally reshapes operational standards by embedding precision and accountability into every stage of the food supply chain. Automated monitoring benefits extend far beyond ticking regulatory boxes—they create proactive safety cultures where potential hazards are identified before they escalate into costly incidents.
How Automated Temperature Monitoring Improves HACCP Compliance becomes evident through measurable outcomes: reduced spoilage rates, enhanced product consistency, and strengthened consumer confidence. Businesses implementing these systems report fewer audit findings, lower insurance premiums, and improved staff engagement with safety protocols.
The investment in automated solutions delivers returns through:
- Protection of brand reputation in an era of instant social media scrutiny
- Competitive advantage through demonstrable commitment to quality
- Long-term cost savings from prevented recalls and waste reduction
Ready to elevate your HACCP compliance programme? Explore automated temperature monitoring solutions that align with your operational needs and regulatory requirements today.
Learn about: How Temperature Monitoring Devices Support Food Safety Training
FAQs
Automated temperature monitoring uses digital sensors and data loggers to continuously track temperatures in food storage, production, and transportation, reducing reliance on manual checks and ensuring HACCP compliance.
It tracks critical control points continuously, generates verifiable records, sends real-time alerts for deviations, and provides audit-ready reports to maintain compliance with food safety regulations.
Manual checks can miss critical periods, introduce human error, produce incomplete records, and leave gaps in monitoring that may result in food safety violations or spoilage.
Common sensor types include probe sensors (internal food temperatures), ambient sensors (air temperature), surface sensors (equipment surfaces), and immersion sensors (liquid products).
Benefits include continuous monitoring, real-time alerts, accurate tamper-proof records, labour cost savings, enhanced operational efficiency, and improved staff accountability.
By maintaining temperatures within safe limits, it prevents bacterial growth in the “danger zone” (5°C–60°C), reducing risks from pathogens like Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli.
They are used in food manufacturing, cold storage facilities, transportation of perishable goods, restaurants, commercial kitchens, healthcare food services, and pharmacies storing temperature-sensitive products.
Systems automatically log temperature readings with timestamps, create audit-ready digital records, generate customizable compliance reports, and maintain long-term historical data for inspections.
Yes, it provides real-time feedback on temperature deviations, demonstrates the impact of errors, supports performance reviews, and fosters a proactive food safety culture without punitive measures.
Key features include high-accuracy sensors (±0.1°C), frequent automated data logging, real-time alerts, cloud-based data storage, customizable reporting, and integration across multiple zones in the supply chain.