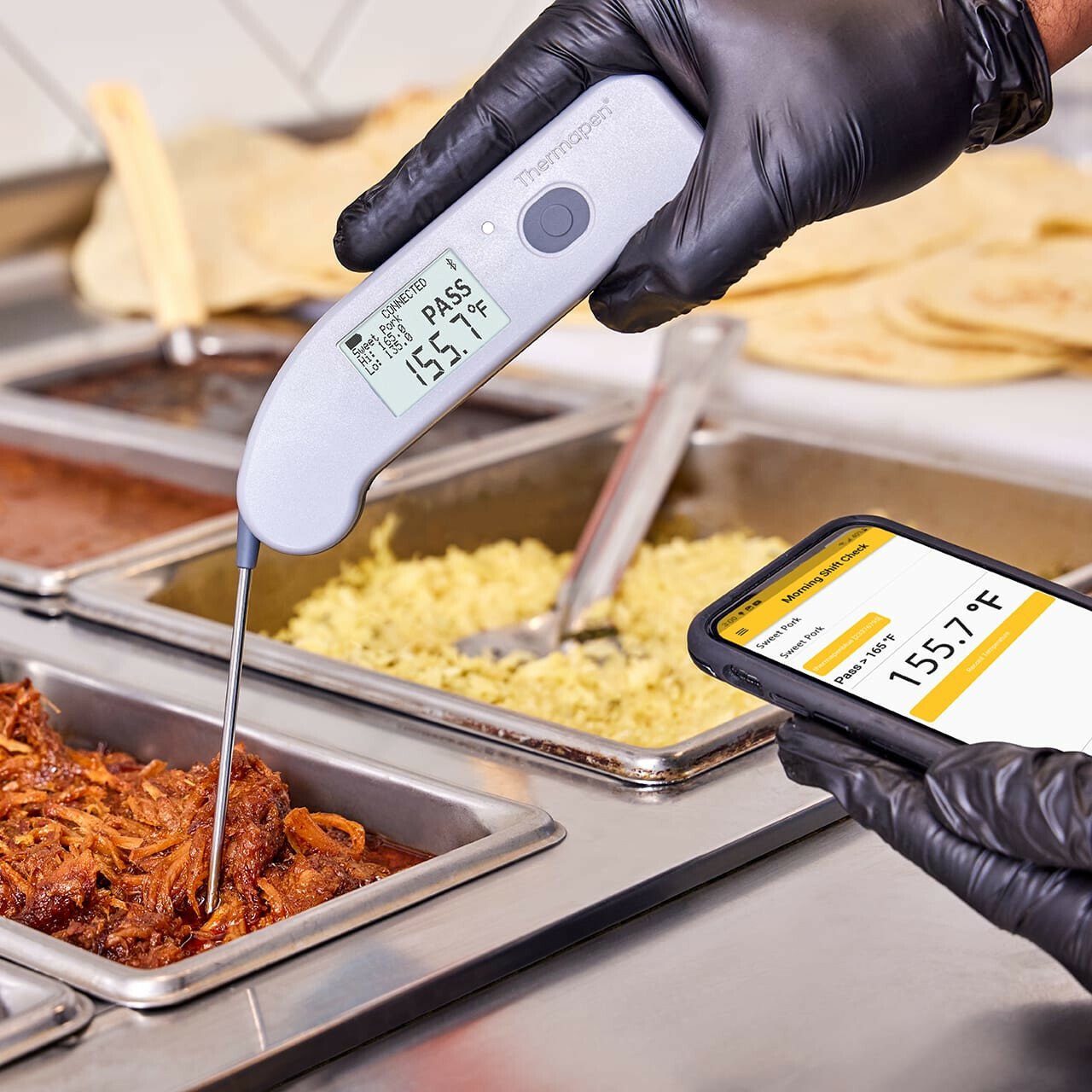
How Do Temperature Monitoring Devices Contribute to Effective Food Safety Training?
Temperature monitoring devices transform food safety training from theoretical knowledge into practical, data-driven learning experiences. These tools provide staff with immediate feedback on their temperature control practices, making abstract concepts tangible and measurable.
Food safety training prevents an estimated 40% of foodborne illness outbreaks when properly implemented. Temperature control sits at the heart of this training because bacterial growth accelerates rapidly when food enters the danger zone between 5°C and 60°C. A single lapse in temperature management can multiply pathogens to dangerous levels within hours.
Modern temperature monitoring devices serve three critical functions in training programmes:
- Real-time verification of proper food handling techniques
- Documented evidence for HACCP compliance and Standard 3.2.2A requirements
- Immediate correction opportunities when temperature deviations occur
These devices bridge the gap between classroom instruction and operational reality, giving trainees confidence in their ability to maintain microbiological safety standards throughout food preparation, storage, and service.

What Are Temperature Monitoring Devices and How Do They Work?
Temperature monitoring devices are specialised instruments designed to measure and record food temperatures throughout storage, preparation, and service. The food industry relies on several distinct types to maintain safety standards.
Common device categories include:
- Digital probe thermometers – handheld tools for spot-checking internal food temperatures
- Infrared thermometers – non-contact devices measuring surface temperatures instantly
- Data loggers – standalone units recording temperature readings at set intervals
- Wireless sensors – connected devices transmitting continuous temperature data to central systems
Real-time tracking capabilities distinguish modern monitoring solutions from traditional methods. Wireless sensors positioned in refrigerators, freezers, hot holding units, and transport vehicles capture temperature readings every few minutes. These measurements transmit automatically to cloud-based platforms where managers can view live data from any location.
The technology operates through thermocouples or thermistors that detect temperature changes and convert them into digital signals. Advanced systems integrate multiple sensors across different storage zones, creating comprehensive monitoring networks. When temperatures drift outside predetermined safe ranges, the system generates instant alerts via SMS, email, or app notifications.
This precision eliminates guesswork in temperature management. Staff receive accurate readings within seconds, enabling immediate corrective action before food safety becomes compromised. The continuous data stream creates detailed records proving compliance during health inspections and internal audits.
Why Is Temperature Control Essential in Food Safety Training?
Temperature control directly determines whether harmful bacteria multiply to dangerous levels or remain safely suppressed. Pathogenic microorganisms such as Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli thrive in the “danger zone” between 5°C and 60°C, where they can double in number every 20 minutes under optimal conditions.
Food safety training must emphasise maintaining safe temperature ranges because improper temperature management accounts for a significant proportion of foodborne illness outbreaks. When staff understand how quickly contamination can occur, they become more vigilant about monitoring and corrective actions.
Critical temperature thresholds in food handling include:
- Cold storage below 5°C to slow bacterial growth
- Hot holding above 60°C to prevent pathogen multiplication
- Rapid cooling from 60°C to 21°C within two hours, then to 5°C within four additional hours
- Cooking to core temperatures that eliminate pathogens (typically 75°C or higher)
HACCP compliance requires identifying temperature control as a critical control point, making it a non-negotiable element of food safety standards. Training programmes that incorporate temperature monitoring devices provide staff with practical skills to verify these thresholds consistently.
The connection between temperature abuse and foodborne illness is immediate and measurable. Even brief exposure to unsafe temperatures can compromise food safety, which is why training must instil both knowledge and the discipline to monitor temperatures throughout every stage of food preparation, storage, and service.
How Do Temperature Monitoring Devices Enhance Compliance with Food Safety Standards?
Temperature monitoring devices generate documented evidence that food businesses maintain proper temperature controls at HACCP critical control points. These food safety management tools automatically record temperature data at regular intervals, creating an auditable trail that demonstrates adherence to regulatory requirements without relying on manual logging systems prone to human error.
HACCP critical control points require specific temperature thresholds to prevent pathogen growth. Monitoring devices verify that:
- Cold storage units maintain temperatures below 5°C for chilled foods
- Hot holding equipment keeps food above 60°C during service
- Cooling processes follow the two-stage cooling method within prescribed timeframes
- Reheating reaches minimum 75°C throughout the food
Australia’s Standard 3.2.2A mandates food businesses implement food safety management tools appropriate to their operations. Digital temperature monitoring systems satisfy this requirement by providing continuous oversight of temperature-sensitive processes. The devices timestamp each reading, eliminating disputes about when temperature excursions occurred.
Regulatory compliance becomes streamlined when inspectors review device-generated reports during audits. The data proves that businesses actively monitor critical control points rather than retrospectively recording temperatures. This proactive approach to How Temperature Monitoring Devices Support Food Safety Training demonstrates commitment to food safety standards whilst reducing the administrative burden on staff who would otherwise spend considerable time maintaining paper-based temperature logs.
How Do These Devices Support Practical Food Safety Training?
Temperature monitoring devices turn theoretical food safety concepts into real-life, hands-on learning experiences that staff can immediately apply in their daily operations. By including these tools directly into training programmes, employees gain practical skills in measuring, recording, and responding to temperature data rather than simply memorising guidelines.
Hands-on learning
With temperature monitoring equipment, trainees can:
- Practice proper probe insertion techniques on various food items
- Identify critical temperature zones for different food categories
- Interpret digital displays and understand temperature readings in context
- Respond to simulated temperature deviation scenarios
Calibration training
Calibration training is a vital part of device-based education. Staff learn to verify accuracy using ice-point or boiling-point methods, ensuring their measurements remain reliable. This technical skill builds confidence in using equipment correctly and recognising when devices require maintenance or replacement.
Staff education
Staff education goes beyond basic operation to include understanding why specific temperatures matter. When trainees use monitoring devices to check food during cooking, cooling, or storage, they witness first-hand how quickly temperatures can shift into danger zones. This hands-on approach reinforces the connection between temperature control and microbiological safety, making abstract concepts like pathogen growth rates more concrete and memorable for food handlers at all skill levels.
How Do Wireless Temperature Monitoring Solutions Improve Operational Efficiency?
Wireless monitoring systems eliminate the need for manual temperature checks by automatically collecting data around the clock. These solutions use sensors placed in refrigerators, freezers, hot holding units, and storage areas that transmit readings to cloud-based platforms, creating a seamless flow of information without requiring staff to physically visit each location.
Continuous data collection provides several operational advantages:
- Reduces labour costs by minimising time spent on manual logging
- Creates comprehensive temperature records automatically for audit trails
- Identifies patterns and trends that help optimise equipment performance
- Eliminates human error associated with manual recording
Instant alerts represent a critical efficiency gain for food businesses. When temperatures drift outside safe ranges, the system immediately notifies designated staff via SMS, email, or mobile app notifications. This rapid response capability allows teams to address issues before food spoilage occurs, preventing costly product losses.
The technology also streamlines compliance documentation. Instead of maintaining paper logs that require manual review and storage, wireless systems generate digital records that can be accessed instantly during health inspections. Food safety supervisors can review multiple locations simultaneously from a central dashboard, making oversight more efficient and enabling faster decision-making when corrective actions are needed.
What Role Do Food Safety Supervisors Play When Using These Devices?
Food safety supervisors play a crucial role in ensuring that temperature monitoring technology is used effectively and that procedures are followed consistently in daily operations. Their main responsibility is to make sure that all staff members are using the monitoring devices correctly and responding appropriately to temperature alerts. This is essential for keeping potentially hazardous foods within safe temperature ranges during preparation, storage, and service.
Operational Oversight
Supervisors have a broader role than just monitoring. They also need to:
- Review device-generated records every day to spot any patterns of temperature deviations
- Conduct spot checks to verify that the sensors are accurate and properly placed
- Investigate alerts promptly and document any corrective actions taken
- Train new staff on how to operate the devices correctly and calibrate them when necessary
- Maintain calibration schedules for all equipment used to measure temperature
Importance of Device-Generated Data
The data generated by the devices is extremely valuable during performance reviews and regulatory audits. Food safety supervisors carefully analyse the temperature logs to evaluate how well the staff manages temperatures. This helps them identify team members who may need additional training. The digital records also serve as concrete evidence of compliance with critical control points, showing auditors and health inspectors that due diligence has been exercised.
Moreover, these records play a significant role in adhering to HACCP principles, which are essential for maintaining food safety standards.
Translating Data into Actionable Insights
The supervisor’s role in How Temperature Monitoring Devices Support Food Safety Training involves converting raw temperature data into insights that can be acted upon. By regularly reviewing trends and promptly addressing any instances of non-compliance, supervisors establish systems of accountability that reinforce proper practices for controlling temperatures throughout the organisation.
How Do Temperature Monitoring Devices Foster a Culture of Proactive Food Safety?
Temperature monitoring devices shift food safety from reactive problem-solving to proactive food safety management by identifying potential hazards before they escalate. Real-time alerts enable immediate intervention when temperatures drift outside safe zones, preventing contamination rather than responding to it after the fact.
This technology creates accountability through visible, measurable data that staff can review throughout their shifts. When team members see temperature trends and patterns displayed on dashboards, they develop heightened awareness of how their actions directly impact food safety outcomes. The transparency builds ownership over temperature control responsibilities.
Risk reduction becomes systematic rather than sporadic. Continuous monitoring eliminates the guesswork from manual checks, catching gradual equipment failures or door seal issues that might otherwise go unnoticed for hours. Early detection of these deviations allows maintenance teams to address equipment problems before they compromise entire batches of food.
The documented history of temperature compliance also reinforces positive behaviours during team meetings and training refreshers, demonstrating the tangible impact of proper protocols on maintaining safe food handling environments.
Conclusion
How can businesses maximise food safety training benefits through technology? By integrating temperature monitoring devices into comprehensive training programmes, food businesses create measurable improvements in staff competency and regulatory compliance. These tools transform abstract food safety concepts into tangible, data-driven practices that employees can immediately apply.
The technology integration in food safety extends beyond simple monitoring—it builds accountability, provides audit-ready documentation, and reduces foodborne illness risks through consistent temperature control. When staff understand how temperature monitoring devices support food safety training, they become active participants in protecting public health rather than passive rule-followers.
Ready to strengthen your food safety culture? Invest in wireless monitoring solutions and structured training that empowers your team with both knowledge and the right tools to maintain the highest safety standards across all operations.
Learn about: How Automated Temperature Monitoring Improves HACCP Compliance
FAQs
Temperature monitoring devices are tools such as digital probe thermometers, infrared thermometers, data loggers, and wireless sensors that measure, record, and transmit food temperatures to ensure safe handling, storage, and service.
They provide hands-on, data-driven learning by giving staff real-time feedback, allowing them to practice proper temperature control techniques and understand the impact of deviations on food safety.
Maintaining temperatures outside the danger zone (5°C–60°C) prevents bacterial growth, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses from pathogens like Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli.
Devices automatically log temperature data at critical control points, generate auditable records, and provide evidence that staff are consistently following food safety standards.
Common devices include:
Digital probe thermometers (handheld)
Infrared thermometers (non-contact)
Data loggers (interval recording)
Wireless sensors (continuous monitoring via cloud platforms)
Wireless systems automatically collect temperature data, reduce labour costs, eliminate human error, provide instant alerts, and generate audit-ready digital records accessible from any location.
Supervisors oversee correct device usage, review data logs, investigate alerts, train staff, maintain calibration schedules, and translate data into actionable insights to ensure compliance and accountability.
They shift the approach from reactive to proactive by providing real-time alerts, continuous monitoring, and visible data, enabling staff to prevent contamination before it occurs.
Staff learn to interpret readings, insert probes correctly, respond to deviations, and understand why temperature thresholds matter, reinforcing practical food safety skills beyond theoretical knowledge.
Benefits include improved regulatory compliance, reduced foodborne illness risk, enhanced staff accountability, audit-ready documentation, operational efficiency, and a stronger food safety culture.


